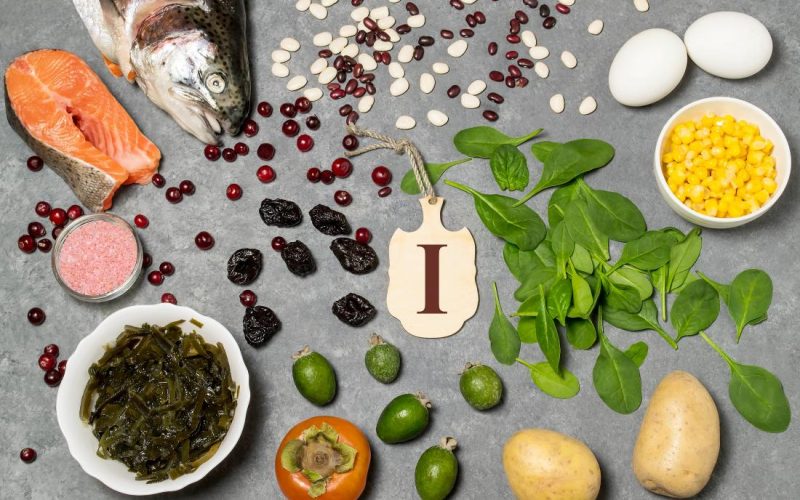
Iodine is an essential mineral that is required by the body in trace (little) amounts. Your body uses this mineral for normal growth and development.
Your thyroid gland stores about 60% of Iodine in your body, the rests are distributed among other body parts.
Iodine plays a very critical role in the health and functions of your thyroid gland, the organ responsible for secreting thyroid hormones to control the metabolic rates and processes of the body.
Without this important mineral, Iodine, your body cannot manufacture thyroid hormones. Iodine controls how your thyroid gland functions, it helps to body to utilize calories effectively thereby preventing fat storage and obesity.
Iodine also aids the removal of toxins in the body and helps your body utilize important minerals such as silicon and calcium.
Amazing Health Benefits of Iodine
The main function of iodine is to aid metabolism and ensure proper development in human being. Below are some of the important health benefits of this amazing mineral.
Boosts your immune system
Iodine is widely known for its important effect on the thyroid gland, but its immense immune-boosting effect is not well-known. This vital mineral is a major booster of the human immune system.
Iodine scavenges free radicals in the body and expels them, it boosts and increases the activities of antioxidants in your body, this helps in producing a strong defense against a wide range of chronic diseases and pathogens.
In studies, iodine protected the brain cells of rats from the harmful effect of free radicals, it did this by connecting the brain cells to fatty acids in the cell membrane, this left less room for the free radicals to attack the brain.
Prevents goiter
Goiter is one of the most common signs of iodine deficiency in the body. Increase your intake of iodine-rich foods to keep this disease at bay.
Examples of foods rich in iodine are seafood, salt, farm-raised dairy and dairy products, and eggs. Good nutrition is used in treating enlarged thyroid gland.
Regulates metabolism
Iodine greatly influence your thyroid glands, it does this by helping in the production of thyroid hormones which directly control the metabolic rate of your body.
Regular process in the body like sleep cycle, food absorption, and the transformation of food into usable energy, and even the efficacy of your organs are controlled by this metabolic rate which heavily depends on iodine.
Certain thyroid hormones like thyroxine and triiodothyronine influence body weight, temperature, and heart rate. These hormones help your body to maintain its basic metabolic rate (BMR) and they also help in protein synthesis.
The normal creation and distribution of these thyroid hormones leads to healthy bodies.
Boosts cognitive functions
Iodine in the body helps one think and perceive correctly, a drop in the levels of iodine in your body would affect the activities of your brain.
Studies performed on people with cognitive problems noticed instant improvement when their intake of iodine was increased. Adults had increased productivity and little children had better cognitive capabilities.
Prevents hypothyroidism
This is one of the most widely known benefits of hypothyroidism, a condition caused by an underactive thyroid gland. This condition slows down all the biochemical processes of your body because the chemical balance has gone off track.
One of the most common consequences of hypothyroidism is increased weight gain. This happens because the ability of the burn off calories and turn them into energy has been affected.
This is why hypothyroidism comes with weight gain and low levels of energy and one of the main causes of hypothyroidism is a deficiency in iodine.
Other effects of hypothyroidism on the body are dry skin, chronic fatigue, constipation, difficulty concentrating, swelling of the legs, and cramps.
Hypothyroidism has to be treated early or else it can lead to coma or heart failure.
Protects against radiation
Iodine prevents your thyroid gland from absorbing radioactive elements, this protects this important organ from radiation injury.
This protective effect of iodine is handy and helpful in cases of disaster at a power plant or nuclear leakage. Doctors also use iodine to treat people suffering from radiation injury.
Boosts energy
Iodine helps optimize the energy levels of your body, it does this by ensuring that your body effectively utilizes calories and nutrients absorbed from foods.
It prevents calories from being stored as fats, all these energize you and prevent obesity which leads to low energy.
Nail health
Iodine boosts the health of your nails and one of the ways iodine deficiency can be known is by looking at the nails. People deficient in iodine have weak and brittle nails.
Fibrocystic breast disease
Studies have shown that women who have fibrocystic breast disease are deficient in iodine. When these women increased their intake of iodine, there was a reduction in the signs and symptoms of this disease.
Oral health
Iodine is of great benefit to your mouth, it has antibacterial properties and this helps to kill harmful bacteria that can cause tooth decay, tooth dullness, plaque, and gum diseases.
It cleanses your mouth and strengthens your teeth. It makes sure your teeth are healthy and it also keeps your mouth odor-free and fresh.
Skin and hair benefits
The body uses iodine to form healthy glowing skin, hair, and teeth. A deficiency in this important mineral would lead to hair loss, teeth, and skin problems.
Iodine keeps skin dryness at bay by regulating the moisture content of the skin, the body uses this vital mineral to form a healthy and radiant skin.
It promotes skin repairs and heals scars and cuts. Iodine controls the hormones that cause acne, it delays aging and clears the signs of aging off your face like wrinkles and fine lines.
Iodine boosts the health of your hair by speeding its growth and increasing the strength of your hair follicles. It kills the fungus that attacks hair follicles and its antiseptic properties protect your scalp from infection.
This provides a clean space for the growth of long and lustrous hair.
Anti-cancer effect
A 2017 study published in the journal of cancer shows that a deficiency of iodine increases the risks of breast cancer. Iodine also prevents a very dangerous form of cancer, thyroid cancer.
Patients of thyroid cancer often notice that their symptoms improve when they increase their intake of iodine. Healthy intake of iodine through foods will reduce your risks of cancers, especially that of the breast and thyroid.
Studies reveal that cancer cells shrink when they are injected with iodine, in most cases, they undergo apoptosis (automatic cell death) and healthier cells replace them.
Many studies have revealed that apoptosis induces programmed cell death (known as apoptosis) in unhealthy and damaged cells in the body. This helps the body form new organs, remove malignant cells like diseased or cancerous cells which can cause fatal conditions to the individual.
Iodine can carry out all these effects on the body because it controls the thyroid gland and even regulates the secretion of hormones.
Supports healthy pregnancy
Iodine boosts a healthy pregnancy free of problems. One important function of iodine in pregnant women is that it prevents stillbirth. It also prevents certain neuro-conditions like cretinism in babies.
That’s why pregnant women need a sufficient amount of iodine in their bodies. Iodine insufficiency in pregnant women can lead to gestational diabetes and this can cause a lot of complications in newborn babies.
Iodine will make sure the fetus grows and develop properly, especially in speech and hearing abilities and it also ensures proper movement of the baby.
Also, a deficiency of iodine in women of reproductive age can make them infertile. Women need optimum levels of iodine in their bodes for their own well-being and that of their babies.
Even after childbirth, the newborn baby still needs iodine and he/she gets this through the mother’s breast milk. If the mother is deficient in iodine, the baby will also be deficient and this will definitely affect the growth and development of the baby.
Pregnant and nursing mothers need to take in more iodine on a daily basis because they can lose more than their required dose of iodine daily. This can lead to serious iodine deficiency in women after pregnancy and breastfeeding are over.
Eliminates Toxins
Iodine has a detoxifying effect on the body, it helps expels heavy metals and harmful chemicals from the body, this include lead, fluoride, mercury, and even biological toxins.
Iodine also has antibacterial properties, and it is highly effective against H. pylori, a pathogen that causes a dangerous form of stomach infection and it also leads to gastric cancer.
Natural Sources of Iodine
Potatoes
Baked potatoes have the highest content of iodine than cooked potatoes. A medium-sized potato contains 60 mcg of iodine which is 40% of your recommended daily intake.
Boiled eggs
One large contains 12 mcg of iodine and that’s the 10% of your recommended daily intake.
Grass-feed mik
Milk from farm animals (cows and goats) raised in nature is rich in iodine. Just a glass of this milk, twice daily, one in the morning and the other in the evening can help your daily requirement of iodine.
A medium-sized glass of milk contains 56 mcg of iodine, which is 36% of your daily need.
Bananas
A medium-sized banana contains about 3 mcg of iodine, you can take this sweet fruit on a daily basis.
Iodine is abundant in sea plants and animals, some seafood with high content of iodine are deep-water whitefish, shellfish, and kelp (brown seaweed), all these foods absorb iodine from the sea.
Other common sources of iodine are sardines, tuna, oysters, lobsters, haddock, cod, clams, sea bass, herring perch, halibut, and shrimp.
Garlic, Dulse, Swiss chard, lima beans, sesame seeds, summer squash, turnip greens, soybeans, and green leafy vegetables like spinach. Iodized salt is also a source of iodine and it is added to baked foods.
How to Know When Your Body Is Demanding For Iodine
When you have low levels of iodine in your body or your body is totally deficient in this vital mineral, your body will send warning signals. These warning signals are called the signs and symptoms of iodine deficiency.
Common signs and symptoms of iodine deficiency that can seriously affect the body are:
- Fatigue
- Autism
- Constipation
- Swelling in the neck (goiter)
- Stillbirth in pregnant women
- Coarse skin
- Weaknesses
- Abnormal heart beat
- Decreased fertility
- High sensitivity to cold
- Complications in pregnancy
- Abnormal and unexpected weight gain
- Goiter
- Poor level of perception
- Hair loss
- Irregular periods or heavy menstruation
- Mental retardation also known as intellectual disability
- Frustration and depression
- Difficulties in learning and remembering
- Dry flaky skin
Severe form of iodine deficiency leads to:
- Organ failure
- Irregular thyroid function
According to WHO , iodine deficiency is one of the leading causes of intellectual disability worldwide.
Precautions
The best way to get your iodine is through natural foods, you won’t get iodine toxicity by eating natural foods but the risk of toxicity is high when using iodine supplements.
Overdose of iodine supplements, especially when it’s over 2,000 mg is dangerous and life-threatening, especially for people suffering from tuberculosis and kidney disorders.
You even increase your risk of thyroid papillary cancer if you use iodine supplements excessively or for a long time. Pregnant and nursing mothers should be careful when taking prescribed iodine supplements.
They should stick to the dose and tell their doctor that they don’t intend to take it for a long time. You can increase your levels of iodine through natural foods.
Side effects of iodine overdose are nausea, headache, fast heartbeat, stomach pain, high body temperature, vomiting, diarrhea, thirst, runny nose, etc.
References;