Trauma is a distressing event, whether physical or emotional, that surpasses an individual’s capacity to cope.
Such experiences can include violence and accidents, and dealing with them can be challenging.
However, understanding the different types of trauma can help regain well-being and flourish.
Within this blog post, we aim to delve into the diverse classifications of trauma.
Further, we will delve into the coping methods that enable you to progress toward a more gratifying and healthy existence.
Hence, we encourage you to continue reading for valuable insights.
What is Trauma?
Trauma is the term used to describe the physical or mental response when a person experiences a traumatic incident that surpasses their capacity for coping.
Anyone can experience it, and upsetting events like violence, accidents, or natural disasters cause it.
Traumatic experiences can significantly impact a person’s well-being.
It may cause strong, difficult-to-manage emotions like fear, helplessness, or horror that linger long after the incident.
Trauma’s aftereffects fluctuate from person to person and take many diverse forms. Nightmares, flashbacks, anxiety, and despair are typical symptoms.
And it can result in separation from other people and a loss of interest in previously enjoyable things.
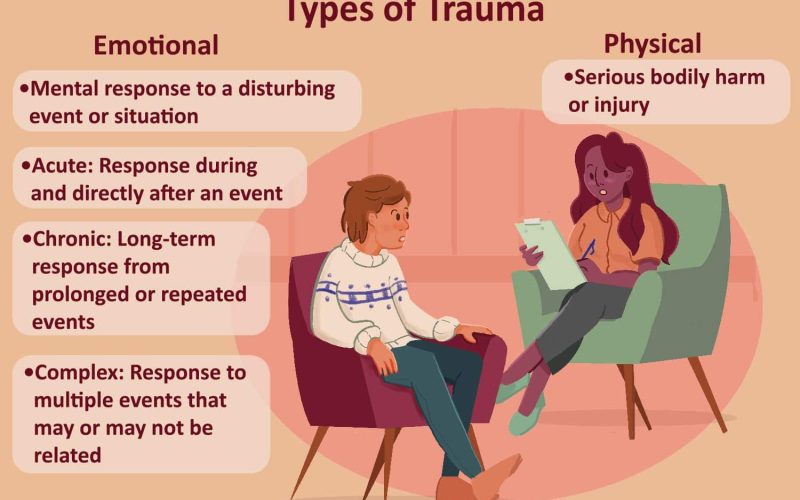
Different Types of Trauma
1. Acute Trauma
Acute trauma is a serious psychological issue that can take root in individuals who experience certain traumatic events.
These include natural disasters, catastrophic accidents, or violent episodes. They can also result from witnessing an event as well.
A few symptoms of this distress are flashbacks, difficulty sleeping, anxiety, depression, and more.
These emotional and physical reactions are normal responses following a terrifying event.
However, they can have lasting impacts if left unaddressed for long enough.
Acute trauma isn’t limited to those suffering from direct experiences. Indirect exposure through hearing about the traumas of others may also produce similar reactions.
Moreover, subtle stressors which occur over time can build up to damaging levels of mental distress.
For example, workplace bullying or extended joblessness could lead to acute trauma-like effects.
Once this is understood, seeking professional help becomes easier.
2. Complex Trauma
Among the different types of trauma is the complex trauma. It results from exposure to many traumatic events, particularly those of an interpersonal nature.
Children often experience it, as it can affect their growth and development.
When children experience complex trauma, it disrupts their ability to regulate emotions effectively.
This can lead to difficulties in forming relationships. It also increases the risk of developing many continuous psychological problems.
Further, complex trauma heightens the potential for developing addictions.
Although it’s possible to recover from the detrimental effects of complex trauma, the damage caused by these traumatic events can be long-lasting.
Types of abuse that can cause complex trauma include:
- Physical abuse
- Sexual abuse
- Verbal abuse
- Emotional abuse
- Domestic violence
3. Chronic Trauma
Chronic trauma is among the different types of psychological trauma responses. Ongoing or repeated traumatic experiences cause it.
And it differs from its counterpart, acute trauma, which results from a single traumatic event such as a car accident or physical assault.
Chronic traumatic events occur over an extended period. Those in disadvantaged living situations often experience them.
Also, they can lead to long-term emotional and physical difficulties that can negatively affect one’s life.
For example, many war survivors experience chronic trauma symptoms, including intrusive flashbacks.
Living with these symptoms often affects a person’s ability to function well. And this can have devastating consequences in their personal and professional life.
Fortunately, though, help is available for those dealing with chronic trauma.
Through counseling, individuals can learn how to cope with their painful memories so they can begin the journey toward healing.
4. Vicarious Trauma
Vicarious trauma is a type of trauma that occurs when individuals are indirectly affected by trauma.
This is possible through witnessing or hearing about the experiences of others. It often affects healthcare providers or therapists who work with trauma survivors.
Continuous exposure to different types of trauma can take a toll on these individuals. Thus, it causes emotional distress and impacts their well-being.
By connecting with trauma survivors and hearing their stories, these professionals may experience similar symptoms.
They may also develop symptoms such as intrusive thoughts, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
Vicarious trauma can challenge an individual’s emotional resilience and ability to cope.
Professionals who engage with trauma survivors must know the potential impact it can have on their mental health.
Taking care of oneself, seeking support from colleagues or supervisors, and engaging in self-care practices are crucial in mitigating the effects of vicarious trauma.
5. Secondary Trauma
Secondary trauma is also among the trauma types that individuals may experience.
It occurs when people are indirectly affected by trauma through close relationships with those who have directly experienced it.
This can happen to trauma survivors’ family members, friends, or caregivers.
When someone you care about has gone through a distressing event, you may become emotionally involved and affected by their experiences.
You may listen to their stories, witness their pain, and provide support during their healing process.
However, in doing so, you can also absorb some of the trauma ourselves, experiencing symptoms like the survivors.
This indirect exposure to this type of trauma may lead to various emotional and psychological reactions.
You may feel overwhelmed, anxious, or depressed and have difficulty sleeping or concentrating.
It’s important to recognize that you can still be significantly impacted even though you haven’t directly experienced the trauma. This way, you’ll be able to cope with the situation.
To cope with secondary or indirect trauma, it’s essential to prioritize self-care and seek support.
This could involve engaging in activities promoting relaxation and well-being, setting boundaries to protect our mental health, and seeking guidance from therapists or support groups.
Can One Person Experience All Types of Trauma at Once?
It is unlikely for one person to experience all types of trauma simultaneously.
Each type of trauma represents a distinct category that arises from different circumstances.
While individuals can experience different types of trauma throughout their lifetime, it would be uncommon for them to occur all at once.
Specific events or ongoing situations influence trauma. These different types of trauma stem from diverse sources and directly impact a person’s well-being.
However, it would be best if you acknowledged that the effects of trauma can overlap and compound over time.
For instance, someone who has experienced acute trauma may be more vulnerable to developing symptoms of vicarious or secondary trauma if they work closely with trauma survivors.
This interaction between different types of trauma can influence an individual’s overall resilience and coping mechanisms.
Bottom Line
Understanding the different types of trauma helps to recognize and address the unique challenges individuals face in their healing journey.
Awareness empowers us to get support, promote resilience, and foster a path toward healing and growth, whether it is acute, chronic, complex, vicarious, or secondary trauma.