Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin also known as pyridoxine, it is a vitamin that your body needs for different essential functions.
It’s significant to the metabolism of fat, protein, and carbohydrate, as well as the creation of neurotransmitters and red blood cells.
Your body is not capable of producing vitamin B6, so you have to obtain it from your diet or from supplements.
Most individuals get enough vitamin B6 from their diet, but some specific populations may be at risk for a vitamin B6 deficiency.
Consuming the right amounts of vitamin B6 is essential for optimal health and may be able to prevent and treat some chronic diseases.
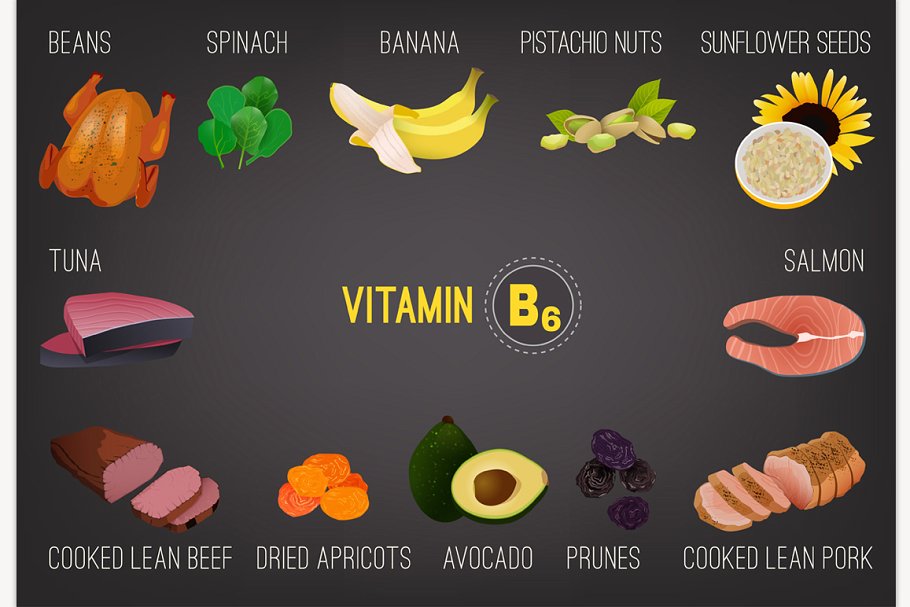
Vitamin B6 Food Sources and Supplements
You can get vitamin B6 from food or supplements.
The present recommended daily amount (RDA) for vitamin B6 is 1.3–1.7 mg for adults older than the age of 19. For most healthy adults, it is possible to get this amount of vitamin b6 through a balanced diet that has some vitamin-B6-rich foods like chickpeas, turkey, tuna, potatoes, salmon, and bananas.
Studies that have highlighted the use of vitamin B6 for the prevention and treatment of health issues so far focus mainly on the use of supplements rather than food sources of vitamin B6.
Doses of 30–250 mg of vitamin B6 every day has been used in studies on PMS, heart disease and morning sickness.
These amounts of vitamin B6 are significantly higher than the Recommended Daily Amount and sometimes when combined with other B vitamins. It is difficult to find out if increasing your intake of B6 from dietary sources offers the same benefits for specific conditions that the supplements may offer.
If you have an interest in taking vitamin B6 supplements for the prevention of health issue, make sure to talk to your healthcare provider about the most advisable option for you.
Also, do not forget to look for a supplement that has been carefully tested for quality by a third party.
9 foolproof health benefits
1. May Improve Mood and also Reduce Symptoms of Depression
Vitamin B6 plays an essential role in the regulation of mood.
This is possible partly because of the fact stars vitamin b6 is vital for the creation of neurotransmitters that help with the regulations of emotions including dopamine, serotonin, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
Vitamin B6 may possibly have a role to play in decreasing high blood content levels of the amino acid called homocysteine , which has been connected to problems like depression and other psychiatric challenges.
Research has shown that symptoms of depression are associated with low blood levels and also low intakes of vitamin B6, mostly in older people who are at high risk for dealing with a B vitamin deficiency.
One research in 250 aged adults revealed that deficient blood levels of vitamin B6 increased the likelihood of depression by two.
However, the use of vitamin B6 for the prevention or treatment of depression has not been found to be effective.
Controlled two-year research in about 300 aged men who did not deal with depression at the beginning revealed that those who were taking a supplement with folate (B9), B6, and B12 were not more or less likely to deal with depressive symptoms when compared to the placebo group.
2. May Promote Brain Health and Reduce Alzheimer’s Risk
Vitamin B6 may also have a role to play in improving brain function and also preventing Alzheimer’s disease, however, at present the research is conflicting.
One thing that has been discovered is that vitamin B6 can reduce high blood levels of homocysteine that may lead to an increase in the risk of Alzheimer’s.
One research in 156 adults who has high homocysteine levels with some mild cognitive impairment revealed that taking some high doses of vitamin B6, B12 and folate (B9) was capable of decreasing homocysteine and also reduce wasting in certain regions of the human brain that are known to be vulnerable to Alzheimer’s.
However, it remains unclear if a reduction in homocysteine will translate to significant improvements in brain function or cause a slower rate of cognitive impairment.
Also, a randomized controlled trial in more than 400 adults who had from mild to moderate cases of Alzheimer’s discovered that high doses of vitamin B12, B6, and folate significantly decreased homocysteine levels but was unable to slow the decline in brain function when compared to a placebo.
Asides the above, a review of 19 studies reached the conclusion that supplementing with only vitamin B6, B12 and folate separately or in combination did not result in any improvement in brain function or even reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s.
More studies that focus on the effect of only vitamin B6 on homocysteine levels and also brain function is required to give a better understanding of the role of the B6 vitamin in the improvement of brain health.
3. May Prevent and Treat Anemia by Aiding Hemoglobin Production
Due to the role of B6 in haemoglobin production, it just may be helpful in the prevention and treatment of anaemia that is caused by deficiency.
Haemoglobin is a protein that delivers oxygen to your cells. When you have low haemoglobin, your cells don’t get enough oxygen. As a result, you may develop anaemia and feel weak or tired.
Several research has connected anaemia with low levels of vitamin B6, especially in pregnant women and women of childbearing age.
However, vitamin B6 deficiency is considered to be rare in most a lot of healthy adults, so there are very limited studies on the use of B6 to treat anaemia.
One case study in a 72-year-old woman who had anaemia as a result of low levels of vitamin B6 discovered that treatment using the most active form of vitamin B6 improved symptoms.
Another study found that taking 75 mg of vitamin B6 daily during pregnancy decreased symptoms of anaemia in 56 pregnant women who were unresponsive to treatment with iron.
More studies are needed to figure out the effectiveness of vitamin B6 in the treatment of anaemia in people other than people who are at increased risk for getting a B vitamin deficiency, such as older adults and pregnant women.
4. May Be Useful in Treating Symptoms of PMS
Vitamin B6 has also been used for the treatment of premenstrual syndrome symptoms, or PMS, including depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Researchers also suspect that vitamin B6 may help with emotional symptoms that are related to PMS as a result of its role in the creation of neurotransmitters that are responsible for regulating mood.
Three-Month research in more than 60 premenopausal women reveals that taking up to 50 mg of vitamin B6 per day improved PMS symptoms of irritability, depression, and tiredness by up to 69%.
However, women who were given a placebo also reported that they had improved PMS symptoms, suggesting that the effectiveness of the vitamin B6 supplement which was recorded may have been partly as a result of a placebo effect.
Another small research discovered that 50 mg of vitamin B6 coupled with 200 mg of magnesium every day significantly reduced the PMS symptoms, which includes irritability, mood swings, and anxiety, over the period of a single menstrual cycle.
While the above results are very promising, they are quite limited by short duration and small sample size. More studies on the effectiveness and safety of vitamin B6 in the improvement of PMS symptoms is required before further recommendations can be made.
5. Vitamin B6 May Help Treat Nausea During Pregnancy
For several decades, vitamin B6 has been used to treat vomiting, and nausea during pregnancy.
In fact, vitamin B6 is an ingredient in Diclegis, which is a medication commonly used for the treatment of morning sickness.
Studies have not entirely revealed why vitamin B6 is helpful with morning sickness, but it is suspected to be because adequate intake of vitamin B6 plays different vital roles in making a healthy pregnancy.
Research in 342 women during their first 17 weeks of pregnancy revealed that a daily 30 mg supplement of vitamin B6 significantly dropped the feelings of nausea after a total of five days of treatment, better than a placebo.
Another study carried out compared the impact of vitamin B6 and ginger on reducing episodes of vomiting and nausea in 126 pregnant women. The outcomes revealed that taking 75 mg of B6 daily decreased vomiting and nausea symptoms by 31% after four days.
These research suggest that vitamin B6 is very effective in the treatment of morning sickness even in time frames of less than a week.
If you’re considering taking vitamin B6 for morning sickness, speak with a medical doctor before you begin any supplements.
6. Vitamin B6 May Prevent Clogged Arteries and Reduce Heart Disease Risk
Vitamin B6 may stop the clogging of arteries and also minimize the risk of heart disease.
Studies have revealed that individuals who have low blood levels of vitamin B6 have almost twice the risk of suffering a heart disease compared to people who have a higher B6 level.
This is likely due to the role of B6 in decreasing elevated homocysteine levels associated with several disease processes, including heart disease.
One research found that rats that were deficient in vitamin B6 possessed greater blood levels of cholesterol and also developed lesions that could lead to artery blockages after they had been exposed to homocysteine, compared to the rats that had an adequate B6 level.
Human studies have also shown a beneficial effect of vitamin B6 in the prevention of heart disease.
A randomized controlled trial that was carried out in 158 healthy grownups who had siblings dealing with heart disease divided participants into two separate groups, one of the groups received 250 mg of vitamin B6 and another group had 5 mg of folic acid on a daily basis for two years and another group that received a placebo.
The study group that was given vitamin B6 and folic acid had lower levels of homocysteine and a lesser abnormal heart tests during an exercise than the group that was on placebo, putting them at a completely lower risk of heart conditions.
7. May Help Prevent Cancer
Getting enough intake of vitamin B6 may reduce your risk of getting some particular types of cancer.
The reason why vitamin B6 may help to prevent cancer remains unclear, but studies suspect that it is related to the vitamin’s ability to fight inflammation that may contribute to the development of cancer and other chronic conditions.
In a review of 12 studies, it was found that both an adequate dietary intake of vitamin B6 and blood levels of vitamin B6 were linked with lesser risks of colorectal cancer. People who had the highest levels of vitamin B6 had in their blood, an almost 50% lower risk of developing this type of cancer.
Studies on the link between vitamin B6 and breast cancer also reveals an association between enough blood levels of B6 and a lesser risk of the disease, most especially in women of postmenopausal age.
However, some other researches on cancer risk and vitamin B6 levels have revealed no association.
More studies that include random trials and not just observational studies is required to correctly assess the particular role of vitamin B6 in the prevention of cancer.
8. Vitamin B6 May Promote Eye Health and Prevent Eye Diseases
Vitamin B6 may also play a major role in the prevention of eye diseases, especially a specific type of vision loss that is known to affect older adults known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Studies have also drawn a link between an increased risk of AMD and high blood levels of circulating homocysteine.
Since vitamin B6 helps with the reduction of high blood levels of homocysteine, consuming enough B6 from your diet may help lower your risk of this disease.
A seven-year study in more than 5,400 female health workers discovered that taking a supplement every day of vitamin B6, B12 and folic acid (B9) significantly dropped AMD risk by 35–40%, when compared to a placebo.
While these outcomes have suggested that vitamin B6 may play a role in the prevention of AMD, it is hard to tell if vitamin B6 alone would provide the same benefits.
Studies have also connected low blood levels of vitamin B6 to visual conditions that block the veins that are connected to the retina. Controlled research in more than 500 people discovered that the lowest blood levels of vitamin B6 were significantly linked with some retinal disorders.
9. Vitamin B6 May Treat Inflammation Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Vitamin B6 may also help lessen symptoms linked with rheumatoid arthritis.
The high amounts of inflammation in the body that comes from rheumatoid arthritis may cause very low levels of vitamin B6.
However, it is very unclear if using vitamin B6 supplements decreases inflammation in individuals with this condition.
A one month study in 36 adults who have rheumatoid arthritis revealed that 50 mg of vitamin B6 every day corrected low blood levels of vitamin B6 but did was unable to decrease the creation of inflammatory molecules in the body.
On another hand, research in 43 adults who had rheumatoid arthritis that was administered 5 mg of folic acid on its own or 100 mg of vitamin B6 coupled with 5 mg of folic acid every day revealed that people who received vitamin B6 had significantly reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory molecules after 3 months.
The contradictory outcomes of the above studies may be as a result of the difference in the dose of vitamin B6 and the length of study.
While it has been discovered that high doses of vitamin B6 supplements may offer some anti-inflammatory benefits for people who have rheumatoid arthritis over an extended period of time, more studies are required.
Potential Side Effects of Taking Too Much Vitamin B6
Getting too excess vitamin B6 from supplements can result in some negative side effects.
The vitamin B6 toxicity may likely not occur from food sources of vitamin B6. This is because It would be almost impossible to consume the amount present in supplements from diet alone.
Taking supplements of more than 1,000 mg of vitamin B6 in a day may lead to nerve damage and even cause pain or numbness in the hands or feet. A couple of these side effects have been documented after consumption of just 100–300 mg of B6 per day.
For all of these reasons, the upper limit of vitamin B6 that is tolerable is 100 mg per day for adults.
The amount of vitamin B6 that is used to manage some health conditions hardly go past this amount. Make sure to consult your doctor If you’re interested in taking above the tolerable upper limit.