Are you an aspiring Biologist or just a knowledge-hungry individual? Understanding the difference between a food chain and a food web will be helpful in whatever category you belong to.
A peaceful and beneficial co-existence between animals and humans requires the latter to understand food chains and webs.
Environmentalists cannot effectively do their job without adequate knowledge of living organisms’ feeding cycle.
Even farmers need to know what’s happening in the environment and their specific habitats of operation.
It’s all intertwined, so keep reading to learn how to tell a food chain from a food web and much more.
But first, let’s define the main terms:
What is a Food Chain?
A food chain is a linear sequence of species where one organism eats another.
The term was coined by an Arab scientist in the 10th century and was later published by Charles Elton in his book “The Ecology of Invasions.” In this case, the predator is eating the prey.
What is a Food Web?
A food web is a complex network of different species interacting with each other through predation, competition for resources, etc.
This organism-to-organism interaction can also occur within a single population.
For example, a fish eats some algae, which are then eaten by zooplankton, the zooplankton eats the fish, and so on. A food web is more like a complex food chain.
What is an Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of plants and animals with the physical conditions (such as temperature, soil, and water) needed to live.
This system has its own set of rules and regulations but no boundaries. The relationships between organisms determine how stable an ecosystem is.
So, what’s the difference between food chains and food webs?
Well, it depends on your perspective. If we take a look at the above definition, we see that there is no major distinction between these two terms. Sometimes, they are used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference.
If we consider a food chain as a linear pathway of predators and prey, the food web would be a network of interactions between them.
However, if we view a food web as a network of interactions among species, the food chain becomes a part of that network.
How to Distinguish Between a Food Chain and a Food Web?
Below is a breakdown of the difference between a food chain and a food web according to:
- The flow of energy
- Number of participants
- The presence or absence of decomposers
- Trophic-level feeding relationships
- Roles to organisms
Energy Flow
The energy flow is one of the main distinguishing factors between food chains and webs. In a food chain, the energy flows unidirectionally from top to bottom.
The primary consumers eat the secondary consumers, who eat the tertiary consumers, and so on.
On the other hand, in a food web, the energy flows interconnectedly. Primary producers feed directly to higher trophic levels.
Secondary producers feed primary consumers, while tertiary producers feed primary and secondary consumers.
Presence Or Absence Of Decomposers
Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organic matter into smaller parts. They play a vital role in recycling nutrients back into the system.
Some examples of decomposers include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, nematodes, arthropods, and earthworms.
In a simple food chain, decomposers are absent because all the nutrients are recycled back to the environment through the food chain.
However, in a food web, decomposers are present. These decomposers help recycle nutrients into the system, thus making the food web more sustainable than a simple food chain.
Trophic Level Feeding Relationships
In a food chain, organisms from the higher trophic level feed on specific organisms from the lower trophic level.
In a food web, one organism on the higher trophic level can feed on multiple organisms on the lower trophic level.
For example, in a food chain, a fish feeds on zooplankton, which feeds on phytoplankton and directly on algae.
But in a food web, a fish may feed on many different types of plankton, including algae, diatoms, dinoflagellates, ciliates, rotifers, and copepods.
Number of Participants
Another difference between a food chain and a food web is the number of participants involved.
A food chain is a simple relationship between producers and primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers.
On the other hand, a food web is a network of interconnected food chains with multiple consumers and decomposers.
Roles to Organisms
The relationships of organisms in a food chain do not affect their competitiveness or adaptability to their environment.
In a food web, organism relationships affect how the participants adapt and compete for existence.
For example, in a food web, there will be a balance between predator and prey. Predators need to consume prey to survive, but they also need to reproduce.
This means predators must have enough food to sustain themselves and produce offspring.
However, prey needs to avoid being consumed by predators. Therefore, prey must find ways to escape predation. Prey may use camouflage or run away from predators.
In contrast, a food chain has no such balance. A predator will always consume its prey. For example, a lion eats a gazelle.
The gazelle cannot escape. It either dies or becomes part of the lion’s diet.
Sustainability
Food webs are more sustainable than simple food chains. It takes longer for a food chain to degrade a resource than for a food web.
In a food chain, the whole process happens very quickly. This is because each species has only one way to obtain nutrition.
If this method fails, then the species cannot survive. However, a species can obtain nutrition from several sources in a food web.
Examples of Food Chains And Food Webs
The following illustrations will make it easier to understand the main difference between a food chain and a food web:
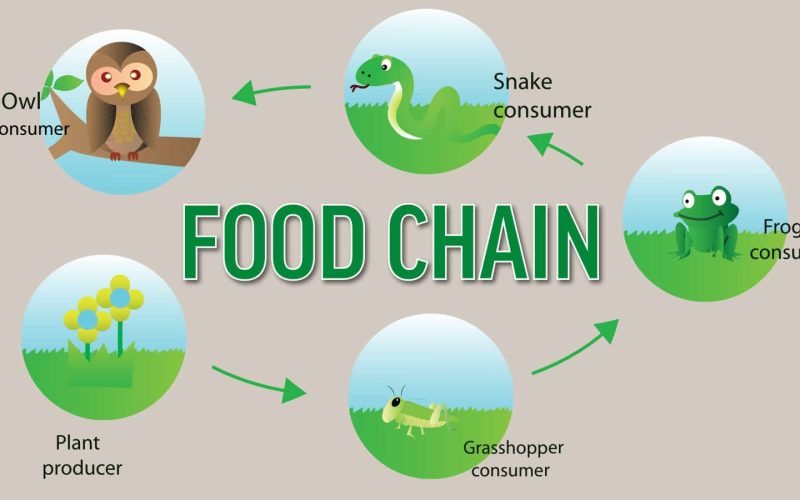
A Simple Food Chain
Green plants (Producer)—Grasshopper (Primary consumer)—Frog (Secondary consumer)—Snake (Tertiary consumer).
This food chain transfers energy from green plants through grasshoppers to frogs to snakes. If any of these three animals die, then the cycle stops.
This is why a food chain is unsustainable. Each animal depends on the others to survive. If any of them fail, then the entire system collapses.
A Simple Food Web
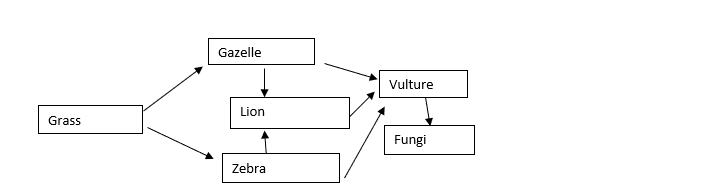
The lion can feed on the gazelle and zebra in the food web, so if one of the prey species dies, the lion does not starve. Instead, the lion consumes the other prey, and life goes on.
Takeaway
There are clear differences between food chains and food webs, although both may seem similar.
The main difference between a food chain and a food web is the path of energy, whereby a food chain is simply linear while a food web is an interconnected network.