Choline is a very important nutrient with a lot of impressive health benefits. Though discovered recently, it is now in the spotlight for its numerous roles it plays in the body.
In 1998, the Institute of Medicine acknowledged this molecule as an essential nutrient, although your body (the liver) can make some of this but it is still necessary you get it from foods to prevent a deficiency.
Choline is not a vitamin or a mineral, it is an organic and water-soluble compound but it is mostly grouped with the B vitamins because they have similarities.
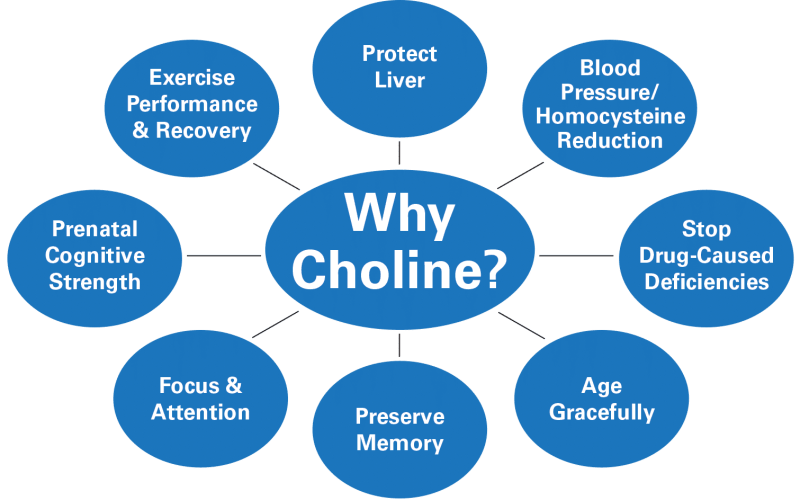
Important Functions of Choline in the Body
Choline has many important roles to play in the body and some of them are:
Heart health: Higher intake of choline has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, choline and folate help convert homocysteine to methionine.
Therefore, a deficiency of choline will lead to the accumulation of homocysteine in your bloodstream and this will increase your risks of heart attack and stroke.
Supports cell structure: This essential nutrient is used in protecting and supporting the structure of your cells and it also protects the integrity of your cell membranes.
Choline increases the ability of the body to absorb fats and fats are used in creating cell membranes and structures. When choline is deficient in your body, the structure of the cells would be affected and the signal messages to other parts of the body will also be affected.
Brain health: Choline is used in making acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter which plays critical roles in intelligence, mood, and memory. It improves brain functions and developments.
It improves information processing and short and long term verbal memory in adult who have poor memory. Choline also improves memory and the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
It is also used in treating depression, dementia, Tourette’s disease, Huntington’s chorea, cerebellar ataxia (a brain disorder), schizophrenia, and some types of seizures.
It helps improve brain development in fetus when taken during pregnancy and it improves visual memory scores in children whose mothers took a higher dose of choline during their second trimester of pregnancy.
Choline also prevent and treat some mental disorders like anxiety, a study showed that lower levels of choline in the body leads to anxiety, mood disorder, and bipolar disorder.
Cell messaging: Choline is used in producing compounds which act as cell messengers, these compounds carry information between the cells of your body.
Liver disease: A deficiency in choline causes liver disease but how it happens is not yet clear. Lower intake of choline also increases the severity of non-alcoholic liver disease.
Another important benefit of choline to the liver is that it helps in transporting fat from the liver to all parts of the body. This helps in cleaning the liver and keeping it fat-free, if not, the fat will accumulate in the liver and cause harm.
It also transports cholesterol and triglycerides from the liver to all parts of the body.
Aid metabolism and transport of fats: Choline helps to eliminate excess cholesterol from your liver, an inadequate amount of choline in your body leads to a buildup of cholesterol and fat in your liver.
Choline is also converted into LDL cholesterol in the liver, though a bad form of cholesterol, a certain amount of it is still needed in the body for optimum function.
When there is an insufficient amount of LDL cholesterol in your liver, fats will be stored and this can lead to fatty liver and liver damage.
Cancer: Some studies have shown that women who have higher intake of choline have lower risks of breast cancer than women who don’t. A lower intake of choline has also been associated with liver cancer.
DNA synthesis: Choline and other B vitamins such as folate and vitamin B12 are involved in the processes for Synthesizing DNA. DNA synthesis is very important for brain development and functions.
DNA is the building block of the body because it is responsible for building the entire body structure. Choline and folate are key nutrients that serve as genetic materials used by the body to build every system.
Neural tube defects: Choline is an essential mineral needed by pregnant women because it reduces the risks of neural tube defects by 51%. It supports a healthy pregnancy and it is one of the most required nutrients for a healthy pregnancy.
In fact, pregnant women need choline more than anyone else because the fetus require choline for proper brain development, nerve channels, and cell structure.
Healthy nervous system: Choline is used in making acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter needed for the movement of muscles, memory, controlling heartbeat, and other functions of the nervous system.
It also helps in nerve signaling and it also maintains the membranes of brain cells. Choline forms tissues that help in brain growth and development, it improves the signaling capacity of nerves, it protects vital neuronal membranes, and supports the structural integrity of your nerves.
Vital for children’s growth and development: Choline is very necessary for neuron plasticity, this is the ability of the brain to create new neuron connection, and choline also supports brain elasticity.
Choline is needed to develop and improve the functions of the brain as children get older, it also plays critical roles in memory, learning, concentration, and logical thinking.
Choline creates neurotransmitter channels in the brain of children to helps information processing, retention, mathematical skills, creative thinking, social clues, verbal abilities, and more.
This vital nutrient is also used to form new brain connections between neurons and they are called synapses, this helps memories to actually form in the brain. Choline prevents learning disabilities in children, it aso improves concentration and ADHD.
Increases energy: choline energizes and it improves physical and sports performance, it also improves muscle functions and it is very important for athletic performance and physical activity.
Choline has a positive effect on your metabolism, it helps the neurotransmitters in the brain to create quicker reaction times and also reduce the amount of time used for mental processing.
It energizes you, improves your sleep, your mood, and it also increases your speed of recovery after a strenuous activity. It prevents fatigue, muscle aches, and pains induced by exercise.
Anytime a muscle moves, choline activates acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, which sends the chemical signals to muscles and make them move.
What Quantity of Choline is Safe?
There is no reference daily intake (RDI) for choline because there is insufficient evidence to back it up, however, the Institute of Medicine set a value for the adequate intake (AI).
This value is envisioned to help healthy people prevent deficiency and its unpleasant consequences like liver problem and damage. These values are just guides and not authoritative because individual requirements are based on hereditary and genetic makeup.
A second reason why the determining the intake of choline is quite difficult is because the accurate quantity of choline in food is unknown.
Below are the recommended AI values of choline for different age groups.
- 0-6 months can take 125 mg of choline daily
- 7-12 months can take 150 mg per day
- 1-3 years can take 200 mg per day
- 4-8 can take 250 mg of choline daily
- 9-13 years can take 375 mg per day
- 14-19 years can take 400 mg daily ( for men) while women need 550 mg daily
- Adult men can take 550 mg per day
- Adult women can take 425 mg per day
- Pregnant women need 450 mg daily while breastfeeding women need 550 mg daily.
Consequences of Choline Deficiency
A deficiency in this vital nutrient can cause harm to your liver, and it also damages your muscles. However, these symptoms are reversed when the one starts getting enough choline through food.
When a pregnant woman is deficient in choline, it increases the risks of miscarriage, low birth weight, premature birth, preeclampsia, and neural tube defect.
Though a lot of people do not consume this nutrient, a deficiency is actually rare. Certain lifestyles and conditions put one at risks of this deficiency and some of them are:
- Pregnancy: The intake of choline during pregnancy should be increased because the developing baby needs this essential nutrient for proper growth and development.
- Athletes: Endurance athletes require sufficient amount of this nutrient because the levels of choline reduces during long and strenuous endurance activities like marathons. Choline delays fatigue.
- Postmenopausal Women: The level of estrogen drops in postmenopausal women and estrogen is used to produce choline in the body.
- High intake of alcohol: Alcohol reduces the levels of choline in your body, therefore alcoholics need to increase their intake of choline and also try and quit.
Possible symptoms of choline deficiency are:
- Mood swings and disorders
- Low levels of energy known as fatigue
- Nerve damage
- Memory loss
- Muscle aches
- Learning disabilities
- Cognitive decline
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver
Side Effects of Choline Supplements
There are dangers in consuming excess of choline supplement but you can hardly have this when most of your choline is gotten through the foods you eat.
Some common side effects of excess choline supplements are fish body odor, sweating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointestinal problems, and low blood pressure. To avoid this, stick to the prescriptions if you are taking supplements.
3,500 mg a day is the daily upper limit for adults and it is impossible to cause harm at this level. It is also impossible for someone to get more than this amount from food, it can only exceed when you take supplement in large doses.
Natural Sources of Choline
Choline is present in a lot of natural foods in the form of phosphatidylcholine and some of them are:
- Soybean: Especially soybean oil, it is very rich in choline. A tablespoon which is approximately 15 ml contains 47.3 mg.
- Chickpeas: A cup of uncooked chickpeas contains 198 mg of choline
- Beef liver: 68 grams of beef liver or 2.4 ounces contains 290 mg of choline.
- Split Peas: A cup of uncooked split peas contains 188mg of choline
- Broccoli: Half cup of broccoli which is approximately 118 ml contains 31.3 mg of choline.
- Navy beans: A cup of raw navy beans contains 181 mg of choline.
- Chicken liver: 68 grams of chicken liver or 2.4 ounces contains 222 mg of choline.
- Grass-fed beef: 78 mg of choline are present in 3 ounces of grass-fed beef.
- Cauliflower: Half cup of cauliflower which is approximately 118 ml contains 24.2 mg of choline.
- Turkey: 3 ounces of turkey contains 57mg of choline
- Eggs: One hard-boiled egg contains 113 mg of choline. A single egg gives you 20 to 25% of your daily needs of choline, 2 eggs gives almost half.
- Chicken Breast: 3 ounces of chicken breast contain 50 mg.
- Salmon: 110 gram or 3.9 ounce fillets gives 62.7 mg of choline.
- Goat milk: One cup of goat milk contains 39 mg of choline.
- Fresh cod: 85 grams or 3 ounces has 248 mg of choline.
- Brussel Sprouts: A cup of raw brussel sprouts contain 17 mg.
It can also be found in breast milk, wheat germ, spinach, peas, beans, nuts, muscle meats, and fish. Choline is also available in the form of additives and supplements, one of the most widely used food additive containing choline is soy lecithin.
Phosphatidylcholine is made from lecithin, and lecithin can be gotten from health stores and pharmacy as a supplement. This lecithin contains 10-20% of phosphatidylcholine.
Phosphatidylcholine is also available as powder supplement or pill and it contains only 13% of choline. Other forms of choline supplements are CDP-choline, Betaine, alpha-GPC, and choline chloride. Alpha-GPC and CDP-choline have higher content of choline per unit weight and they are easily absorbed by the body than other forms of choline.
Increase your intake of choline by eating these foods regularly, you can even increase your intake of eggs and vegetables containing choline. Then, if you must take supplement, it should be under the supervision of a doctor and you have to follow the prescription strictly.
For now the supplement is quite safe as they is no report of it reacting with drugs but to be on a safe side, you have to check with your doctor first to know if it’s safe to take it along with the medication you are on.
Sources;
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2782876/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19906248
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20446114
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12668679
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12193594
- http://www.nap.edu/read/6015/chapter/1
- http://nutritiondata.self.com/foods-000144000000000000000-1w.html
- http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/dairy-and-egg-products/117/2