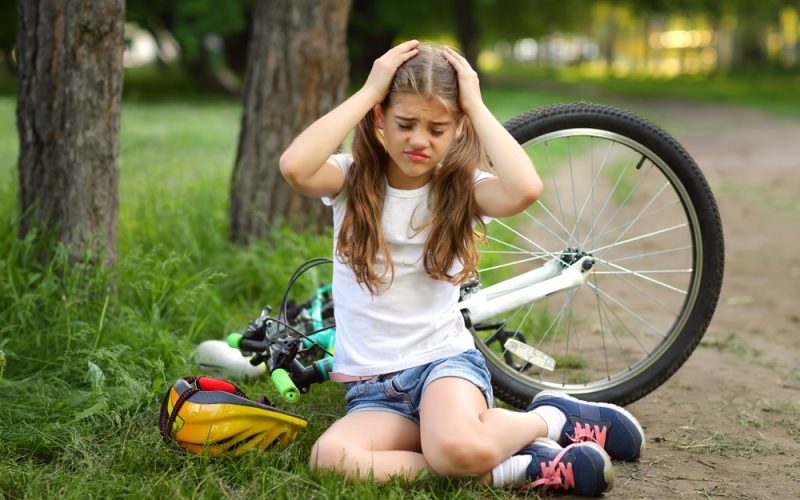
There are different types of concussions. A traumatic brain injury induced by a strong knock, blow, or jolt to the head is known as a concussion.
It can happen due to falls, car accidents, sports injuries, or when something falls on the head.
Even though most concussions are minor and have no long-term consequences, a doctor should check every concussion.
Furthermore, this is particularly significant in the case of youth and sports injuries.
While the subtypes are not mutually exclusive and overlap some symptoms (most concussions begin with a headache, and sleep disruptions and neck pain are common), researchers hope that identifying the unique symptoms of each subtype could lead to more effective therapies for all concussions.
Traumatic brain injuries can result in bruising, blood vessel damage, and nerve injury. Your brain doesn’t work as well as it should.
Also, If you’ve had a concussion, your vision may be blurred, lose balance, or pass out. The brain is perplexed.
Concussions can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Falls, especially in children and the elderly
- Participating in a contact sport
- There is a lack of sufficient safety equipment and monitoring for contact sports.
- Accidents involving a car, motorbike, bicycle, or other vehicles result in a blow to the head, hit, struck with an object, or subjected to physical abuse.
- Service in the military
- A previous concussion
- Concussion Symptoms
Symptoms of Concussion
Diagnosing concussions can be problematic. A concussion is invisible even if you have a cut or bruise on your head. It may take days or weeks for symptoms to show.
Some symptoms last only a few seconds, while others persist for hours.
Furthermore, following a concussion, a person may have various physical, mental, and emotional symptoms.
In addition, the following are symptoms of traumatic brain injury:
- Feeling befuddled or bewildered
- Clumsiness
- Speech slurred
- Vomiting or nausea
- Headache
- Dizziness or difficulty with balance
- Vision is hazy
- Sluggishness
- The ringing in the ears
- Irritability or other personality or behavior changes
- Concentration problems
- Memory lapses
- Tiredness or drowsiness
- Consciousness loss
- Forgetting things, such as repeating oneself, is an example of forgetfulness.
- Questions are being answered slowly.
- Sleep disturbances
- Depression
- Problems affecting the senses of taste and smell
Types of Concussions
1. Cognitive/ Fatigue
This form of concussion can affect lengthy or complex mental tasks, complex subject matter, and long days.
It might sometimes make you feel more tired as the day progresses.
In addition, this is one of the different types of concussions. The following are examples of cognitive issues:
- Concentration slipped.
- Distractibility increased.
- New information is challenging to learn and retain.
- Multitasking abilities are deteriorating.
2. Vestibular
Balance, mobility, and vision can all be affected by this form of concussion.
Furthermore, the vestibular system – the brain’s balance center — is impaired, which affects one’s ability to:
- The motion should be interpreted.
- Make sure your head and eye movements are in sync.
- When moving your head, keep your gaze steady or balanced.
3. Ocular
This is one of the different types of concussion. This sort of concussion can make it challenging to perform visual tasks such as:
- It won’t be easy to read Long passages.
- Observing a computer screen or a mobile phone.
- Ocular shocks affect tandem eye movements, making it difficult to bring one’s eyes together or move one’s eyes to track motion.
4. Post-traumatic Migrane
This form of concussion may cause you to alter your daily schedules, such as sleeping in or avoiding loud concerts or sporting events.
Among the signs and symptoms are:
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Light or noise sensitivity
5. Cervical
Stress or pressure on the neck, spine, or spinal cord is a problem with this concussion form.
It may cause headaches for the rest of your life. Slouching when using a computer or carrying a large backpack can exacerbate symptoms.
6. Anxiety/Mood
This concussion makes it challenging to switch off your mind and produces excessive worry or concern.
Also, this might lead to difficulties with social interaction, which can be exacerbated if you skip usual tasks due to your concussion.
What Happens if a Concussion Goes Untreated?
Untreated concussions can have both immediate and long-term consequences, particularly in the case of moderate or severe concussions, such as:
- Severe brain injury causes edema, which causes the brain to swell and induce coma or death. Because the cranium is a closed space, edema causes pressure accumulation over respiratory and cardiovascular centers (areas in the brain that control breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure), depressing them and causing the individual to slip into a coma or die.
- Post-concussion migraine: Many persons complain of headaches after concussion episodes, especially if the injury was left neglected.
- Post-traumatic epilepsy occurs when a portion of the brain is harmed and changes, resulting in seizures or epilepsy.
- Post-concussion syndrome: Some people experience headaches, dizziness, concentration, and memory issues weeks after a concussion. In addition, Anxiety and phobias, irritability, mood changes, and increased sensitivity to lights and sounds are all symptoms that some people experience. Also, Symptoms appear within the first seven to ten days and subside after three months. Also, they can last a year or longer in some cases.
- Dementia: Following a brain injury, cognitive functions such as cognition, memory, and multitasking capacity may be lost or damaged.